Single mode fiber represents the pinnacle of optical fiber technology, offering unparalleled capabilities in high-speed data transmission over vast distances. Its ability to carry signals with minimal dispersion and attenuation makes it the backbone of modern telecommunications networks, data centers, and internet infrastructure.
In this article, We collected the most common questions among users online and put it simply together with our answers.
What is single mode fiber?
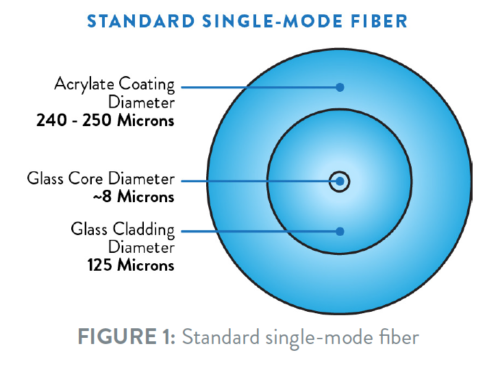
Single mode fiber (SMF) is a type of optical fiber that allows only one mode of light to propagate through its core. It has a small core diameter, typically around 9 microns, enabling high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal signal dispersion.
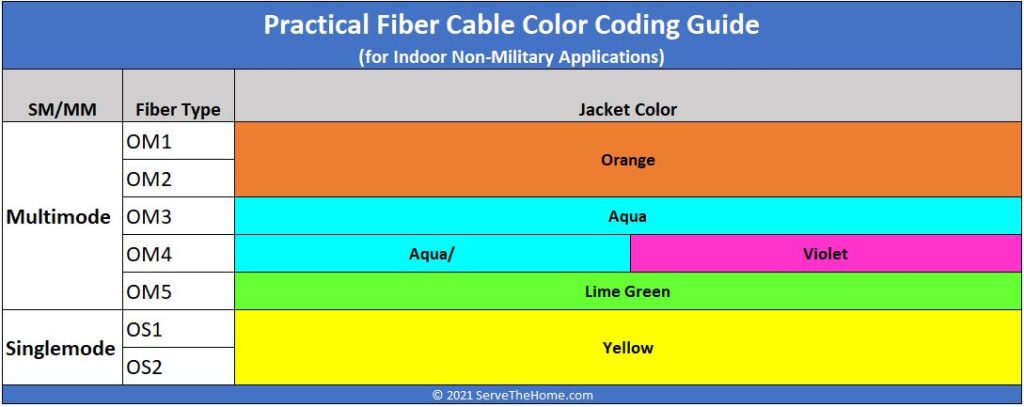
Single Mode Fiber Types: OS1 vs OS2
As we all know, multimode fiber is usually divided into OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 and OM5 fiber types. When it comes to single mode fiber types, it can be categorized into OS1 and OS2 fiber, which are SMF fiber specifications.
OS1 fiber is mainly used in the construction of indoor applications, such as campus networks and building networks, where the maximum distance is 10 km. OS2 fiber is more suitable for outdoor applications including backhaul networks, external plants, FTTH, WDM/DWDM network, etc., where the maximum distance is up to 200 km.
OS1 vs OS2: What are Their Differences?
It’s of great significance to figure out the difference between OS1 and OS2 when conducting deployments. The specification table below will present the differences between them clearly.
| OS1 | OS2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Standards | ITU-T G.652A/B/C/D | ITU-T G.652C/G.657.A1 (part) |
| Cable Construction | Tight Buffer | Loose Tube |
| Application | Indoor | Outdoor |
| Attenuation | 1.0db/km | 0.4db/km |
| Max. Distance | 10 km | 200 km |
| Price | Low | High |
What is the difference between single mode and multimode fiber?
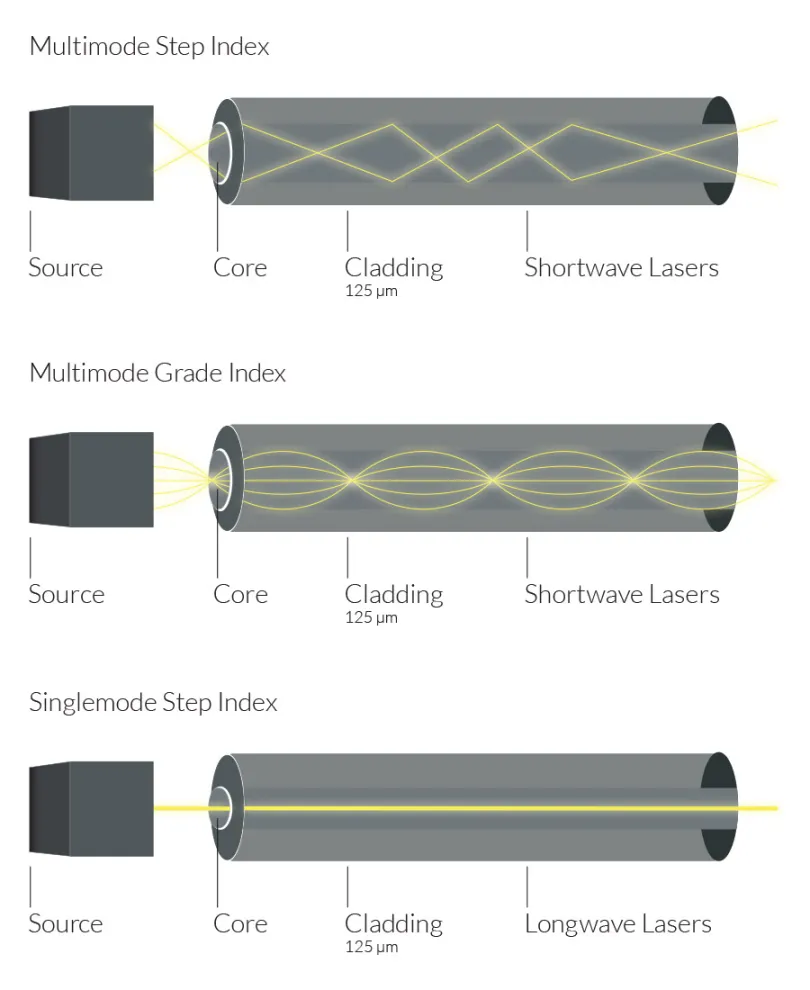
Single mode fiber has a smaller core diameter and supports only one mode of light propagation, while multimode fiber has a larger core diameter and supports multiple modes of light. Single mode fiber is optimized for long-distance transmission, whereas multimode fiber is suitable for shorter distances.
How far can single mode fiber go?
Single mode fiber can transmit signals over much longer distances compared to multimode fiber, reaching up to 100 kilometers (about 62 miles) without the need for signal regeneration. This makes it ideal for long-haul telecommunications and data transmission applications.
Can I use multimode fiber for single mode?
While technically possible, it’s not recommended. Multimode fiber is optimized for shorter distances and operates with different light propagation characteristics than single mode fiber. Using multimode fiber for single mode applications may result in signal loss and poor performance over long distances.
Can I use multimode fiber with single mode SFP?
Using single mode Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) modules with multimode fiber is not recommended. Single mode SFPs are designed to work with single mode fiber, and using them with multimode fiber may lead to compatibility issues and degraded performance.
Can I use single mode fiber for short distance?
Yes, single mode fiber can be used for short distances as well. While optimized for long-distance transmission, it can effectively transmit data over shorter distances without significant issues, offering reliable performance and low signal dispersion.
Can I use single mode fiber with multimode?
While technically possible with special equipment and cables, it’s generally not recommended. Mixing single mode and multimode fibers in the same network infrastructure can lead to compatibility issues and degraded performance, particularly over long distances.
Can multimode fiber be used for single mode?
Using multimode fiber for single mode applications is not recommended. Multimode fiber is optimized for shorter distances and has a larger core diameter compared to single mode fiber, leading to increased signal loss and poor performance over long distances.
Can single mode fiber transmit and receive simultaneously?
Yes, single mode fiber supports bidirectional communication, allowing it to transmit and receive data simultaneously. This is achieved by using separate wavelengths for upstream and downstream data transmission, enabling full-duplex communication over the same fiber optic link.
Can you mix single mode and multimode fiber?
While possible with specialized equipment, it’s generally not recommended. Mixing single mode and multimode fibers in the same network infrastructure can result in compatibility issues, increased signal loss, and degraded performance, especially over long distances.
Can you splice multimode fiber to single mode fiber?
While technically possible with special splicing techniques, it’s generally not recommended. Multimode and single mode fibers have different core diameters and optical characteristics, leading to increased signal loss and degraded performance in the spliced region.
How does single mode fiber work?
Single mode fiber allows only one mode of light to propagate through its core, resulting in a single, straight light path. This minimizes signal dispersion and enables high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal signal degradation.
How many microns is single mode fiber?
Single mode fiber typically has a core diameter of around 9 microns. This small core diameter enables high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal signal dispersion and attenuation.
How to check single mode or multimode fiber?
You can determine the type of fiber by examining its markings or using specialized fiber optic testing equipment. Single mode fiber is typically labeled with “SMF” or “OS1/OS2,” while multimode fiber is labeled with “MMF” or “OM1/OM2/OM3/OM4/OM5.”
How to connect single mode to multimode fiber?
You can connect single mode to multimode fiber using mode conditioning cables or media converters specifically designed for this purpose. These cables or converters adapt the optical characteristics of the fibers to ensure proper signal transmission.
How to differentiate single mode and multimode fiber?
You can differentiate between single mode and multimode fiber by examining their core diameters and markings. Single mode fiber typically has a smaller core diameter and is labeled with “SMF” or “OS1/OS2,” while multimode fiber has a larger core diameter and is labeled with “MMF” or “OM1/OM2/OM3/OM4/OM5.”
How to terminate single mode fiber?
Single mode fiber can be terminated using various methods, including fusion splicing, mechanical splicing, or connectorization with epoxy or pre-polished connectors. These methods provide reliable connections for data transmission.
What color is single mode fiber?
Single mode fiber is typically yellow, although the color may vary depending on manufacturer specifications and industry standards. Yellow-colored jackets are commonly used for single mode fiber cables to distinguish them from multimode fiber cables.
What is single mode fiber used for?
Single mode fiber is used in long-haul telecommunications networks, data centers, and high-speed internet connections. Its ability to transmit data over long distances with minimal signal loss makes it ideal for applications requiring reliable, high-speed data transmission.
What is the acceptable dB loss for single mode fiber?
The acceptable dB loss for single mode fiber depends on the application and industry standards, typically ranging from 0.2 dB/km to 0.5 dB/km. This loss includes both intrinsic fiber attenuation and additional losses due to splices, connectors, and other components.
What is the bandwidth of single mode fiber?
Single mode fiber has a high bandwidth capacity, typically ranging from 100 GHz·km to 200 GHz·km. This allows for high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal signal distortion and attenuation.
What is the core diameter of single mode fiber?
The core diameter of single mode fiber is typically around 9 microns. This small core diameter enables single mode operation, resulting in high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal signal dispersion.
Which of the following is a characteristic of single-mode fiber?
A characteristic of single-mode fiber is its ability to support only one mode of light propagation through the core. This results in a single, straight light path, minimizing signal dispersion and enabling high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal signal degradation.
A single mode fiber is designed to carry which wavelength?
Single mode fiber is designed to carry light in the 1310 nm and 1550 nm wavelength ranges, commonly used in telecommunications and data transmission applications. These wavelengths correspond to the low-loss windows of optical fiber.
Is single mode fiber cheaper than multimode?
Single mode fiber tends to be more expensive than multimode fiber due to its higher performance and specialized manufacturing processes. However, the cost difference may vary depending on factors such as fiber length, installation complexity, and market demand.
What is the maximum distance of single mode fiber?
Single mode fiber can transmit signals over distances of up to 100 kilometers (about 62 miles) without the need for signal regeneration. This long-distance capability makes it suitable for various applications requiring reliable, high-speed data transmission over extended distances.
Conclusion
For more questions about single mode fiber, You can request us and we will keep it updated. If you are looking for fiber optic products, Bativ will be one of your best suppliers in China.