Optical Distribution Frame is often short for ODF, It is a very important fiber optic equipment in fiber optic networks. As it is a good solution for management and distribution of fiber optic cables.
ODFs not only organize and protect fiber optic connections but also provide a centralized location for managing the intricate web of cables that power our connected world. Let’s delve into the essence of Optical Distribution Frames, their components, functionality, and significance in today’s digital age.
What is an Optical Distribution Frame?
An Optical Distribution Frame (ODF) is a cable rack that organizes fiber optic cable connections and terminations. Its primary function is to provide a structured and accessible platform for connecting, managing, and distributing incoming and outgoing fiber optic lines in telecommunications facilities. ODFs are designed to accommodate fiber optic cables and connectors, ensuring that they remain protected, organized, and easily accessible for maintenance or reconfiguration.
Key Components
The anatomy of an ODF is designed to support the complexity and sensitivity of fiber optic connections. Major components include:
- Frames: The structural skeleton that holds the entire setup in place, providing slots or panels for fiber termination units.
- Fiber Termination Units: These are modules within the frame where fiber optic cables are terminated with connectors. They can be in the form of patch panels or splice trays.
- Cable Management Systems: Comprising of trays, guides, and clamps, this system ensures that cables are neatly routed and secured, preventing tangling, bending, and physical damage.
- Locks and Security Features: Many ODFs come equipped with locking mechanisms to secure sensitive connections against unauthorized access.
Types of Optical Distribution Frame?
The most common Optical Distribution Frame types are wall mounted and rack mounted, as its name, it is categorized by its application.
Wall mount ODF usually uses a design like a small box which can be installed on the wall and is suitable for fiber distribution with small counts. Floor mount ODF adopts closed structure. It is usually designed with relatively fixed fiber capacity and nice appearance.

Wall mount ODF
Wall mount ODF usually uses a design like a small box which can be installed on the wall and is suitable for fiber distribution with small counts. Floor mount ODF adopts closed structure. It is usually designed with relatively fixed fiber capacity and nice appearance.
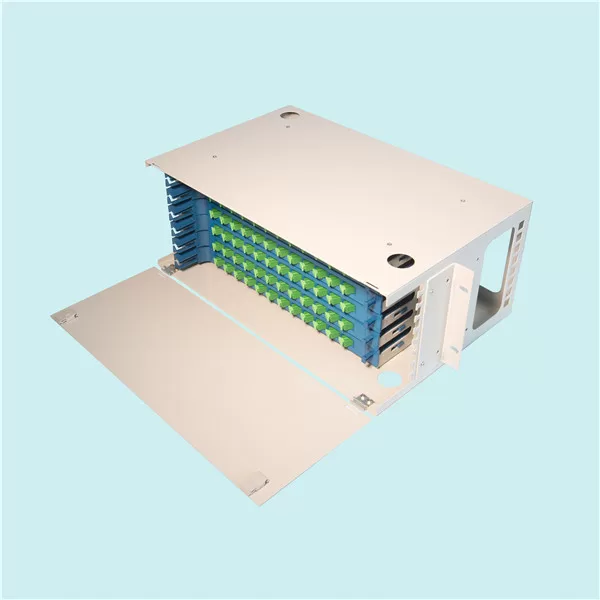

Rack mount ODF
Rack mount ODF is usually modularity in design with firm structure. It can be installed on the rack with more flexibility according to the fiber optic cable counts and specifications. This kind of optical distribution system is more convenient and can provide more possibilities to the future variations. Most of the rack mount ODF is 19”, which ensures that they can be perfectly installed on to the commonly used standard transmission rack.
How to choose an ODF?
There are many factors to be considered when choosing an ODF not only the structure types. The following will tell more factors as the guide for you to choose a suitable one.
Fiber Counts
As the number of fiber connections in places like data center increases, the need for high density ODF becomes the trend. Fiberstore provides ODFs with 24 ports, 48 ports and 144 ports. And we also offer customized service for customers.
Manageability
high-density is the good but management is not easy. ODF should provide an easy management environment for technicians. The basic requirement is that ODF should allow for easy access to the connectors on the front and rear of those ports for insertion and removal. This requires that ODF should reserve enough space. In addition, the color of adapters installed on the ODF should be consistent with the color code of fiber optic connectors to avoid wrong connections.
Flexibility
as mentioned above, rack mount ODF is relatively flexible during applications with the modular design. The adapter port on ODF is also flexible to increase the flexibility. For example, an ODF with ports of duplex LC adapter can be installed with duplex LC, SC or MRTJ adapters. An ODF with ports of ST adapter can be installed with both ST adapters and FC adapters.
Protection
ODF integrates fiber connections in it. The fiber connections like splicing joint, fiber optic connectors are actually really sensitive in the whole transmission network and can directly influence the stability and reliability of the network. Thus, a good ODF should have protection device to prevent fiber optic connections from damages produced by dust or stress.
How Does It Work?
The operation of an Optical Distribution Frame hinges on its ability to centralize fiber optic cable connections. Telecommunication providers bring their fiber optic cables to the ODF, where they are then terminated, organized, and connected as needed. Through patch cords, these connections can be easily reconfigured to route data signals to various destinations, facilitating the dynamic demands of network traffic.
Advantages of Using ODFs
The integration of ODFs into telecommunications infrastructure offers several key advantages:
- Organization: By centralizing fiber optic connections, ODFs eliminate clutter and reduce the risk of cable damage.
- Flexibility: They allow for easy changes in network architecture, accommodating growth and technological advancements without significant disruption.
- Accessibility: Maintenance and troubleshooting become more manageable, reducing downtime and improving network reliability.
- Protection: ODFs provide a controlled environment that protects delicate fiber optic cables from environmental threats and mechanical damage.
- Scalability: They can be expanded or adjusted to meet the evolving needs of a telecommunications network, ensuring future compatibility.
Applications and Importance
Optical Distribution Frames are integral to various settings, including data centers, telecom exchanges, and any facility requiring extensive fiber optic networking. They serve as critical nodes in the vast networks that underpin internet service providers, cellular networks, and enterprise IT systems. In the era of big data, cloud computing, and high-speed internet, the role of ODFs in managing and safeguarding the physical infrastructure cannot be overstated.
The Future of Optical Distribution Frames
As the demand for faster internet speeds and more robust telecommunications networks continues to grow, the development and enhancement of ODFs remain a priority. Innovations in design, materials, and integration with smart technologies are expected to further enhance their efficiency, reliability, and capacity to support the burgeoning needs of the digital world.
Conclusion
Optical Distribution Frames are more than just cable racks; they are the unsung heroes of the telecommunications world, ensuring that the backbone of our digital infrastructure is strong, flexible, and reliable. As we continue to push the boundaries of technology, the evolution of ODFs will remain a cornerstone in the quest to keep the world connected, proving that even in an age of wireless communication, the right connections matter.